Semaglutides now most commonly prescribed GLP-1, varying state-by-state
At athenahealth®, we are uniquely positioned to observe nationwide care delivery trends in near real-time. With over 160,000 providers and $290 billion in annual claims activity across the athenaOne® network, we support care for more than 20% of the U.S. population. That reach — spanning all 50 states and dozens of specialties— creates a robust, connected network that delivers powerful insights into how medicine is practiced and how it's changing.1
Our most recent findings on GLP-1 prescribing trends from 2022 to 2024 tell a story of rapid growth, clinical evolution, and expanding potential. These medications, originally developed to manage type 2 diabetes, are now reshaping how clinicians think about treating obesity, managing chronic conditions, and supporting long-term health outcomes.
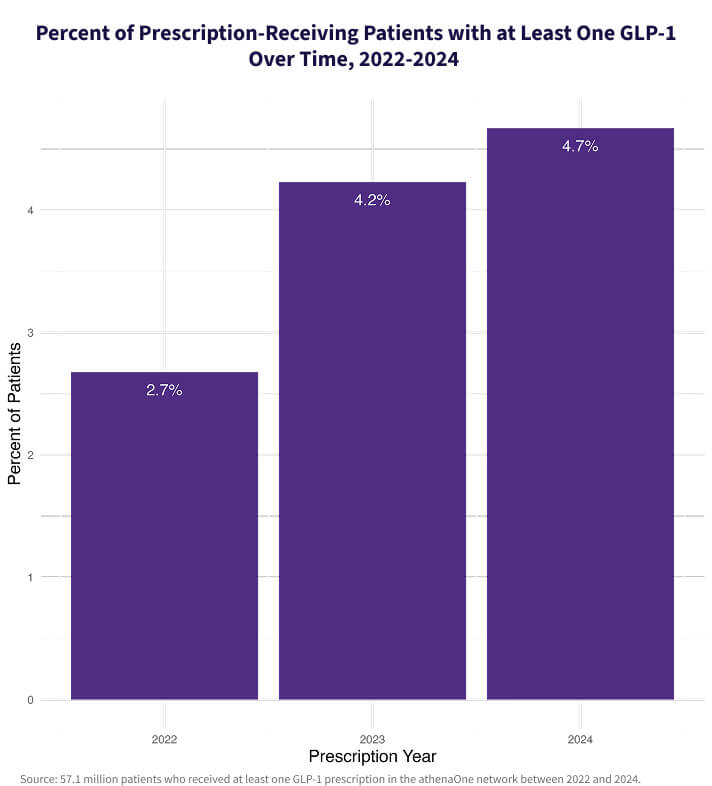
GLP-1 prescribing rose quickly from 2022 to 2024
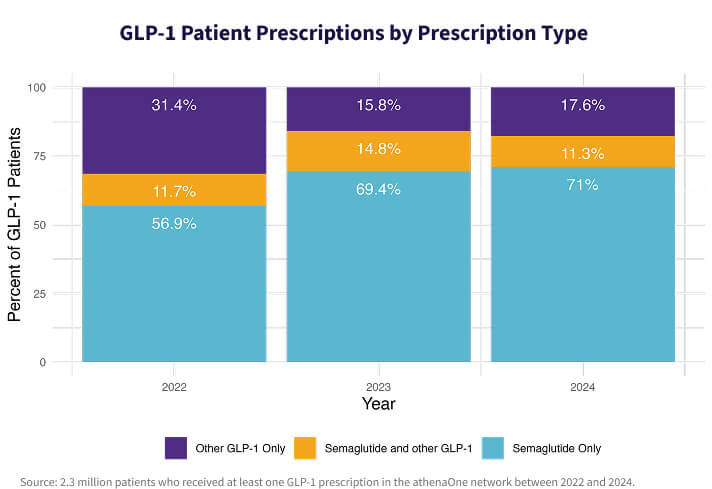
Data from the athenaOne network shows that in 2024, 4.7% of all prescription-receiving patients were prescribed a GLP-1, a 74% increase since 2022. Semaglutides like Ozempic®, Wegovy®, and Rybelsus® have emerged as the most widely used GLP-1s, accounting for 70.9% of all GLP-1 prescriptions in 2024, up from 56.6% in 2022.
It remains rare for patients to be prescribed multiple GLP-1s in a single year, indicating that clinicians are gravitating toward specific agents within the class. Among all GLP-1 patients, semaglutides are becoming the clear preference.
Shifting semaglutide diagnoses from diabetes to obesity
GLP-1s remain most commonly prescribed to patients with diabetes, but our analysis shows an increasing number of patients are receiving these medications to manage obesity, without a diabetes diagnosis.
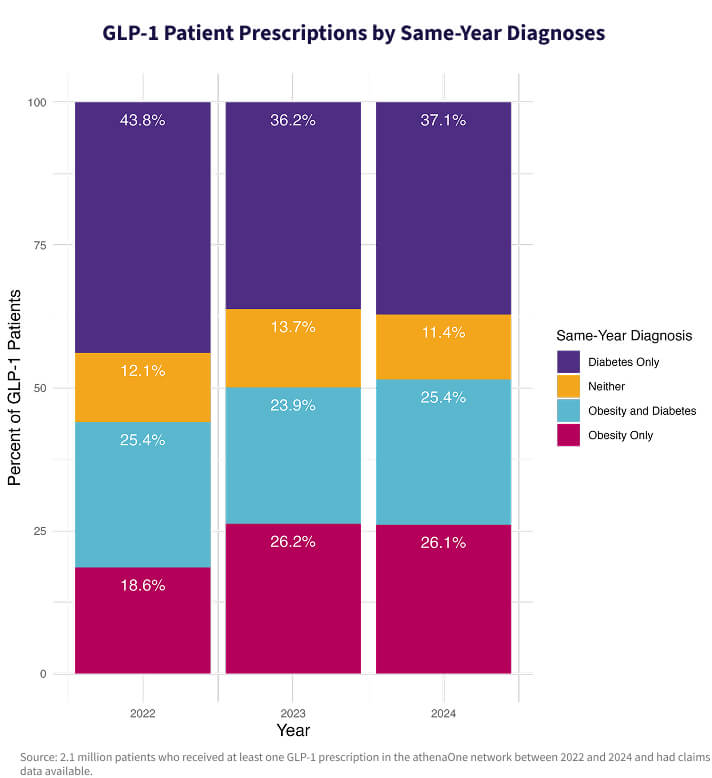
In 2022, patients with obesity but not diabetes made up 18.6% of all GLP-1 patients; by 2024, that number had risen to 26.1%. During the same period, the share of GLP-1 patients with diabetes dropped from 69.2% to 62.9%. Only 11.4% of patients received a GLP-1 prescription without a diagnosis of either diabetes or obesity, a slight decline from previous years—likely due to insurance requirements.
Our most recent findings on GLP-1 prescribing trends from 2022 to 2024 tell a story of rapid growth, clinical evolution, and expanding potential.
GLP-1 use varies widely by state
Regional differences in prescribing are pronounced. In 2024, West Virginia had the highest share of GLP-1 patients in the nation, while New Hampshire experienced the greatest year-over-year growth in GLP-1 prescriptions from 2023 to 2024, with Washington, DC close behind.
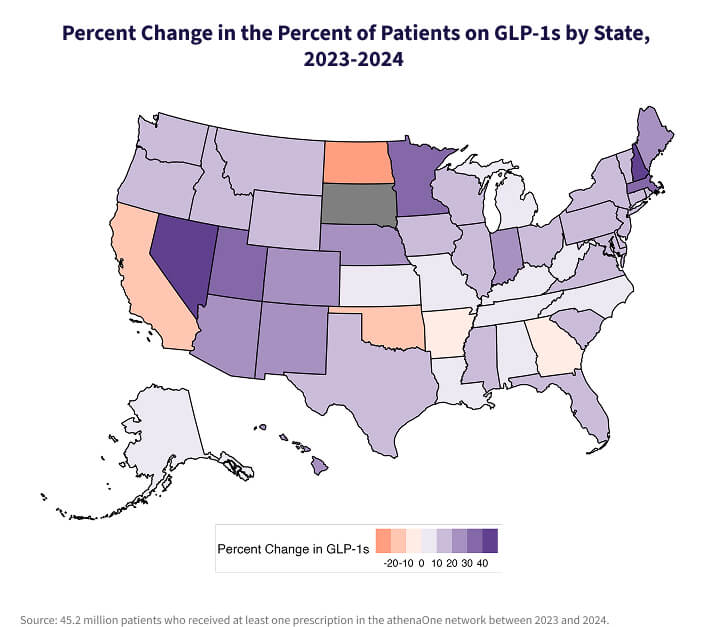
These trends reflect local care patterns, patient demographics, and access considerations, which are particularly relevant in states with high chronic disease burdens or limited specialist availability.
What do changing prescription rates mean for you and your patients?
As GLP-1 use grows, the clinical implications for you and your practice are expanding, too. Clinicians are increasingly navigating questions that extend beyond glycemic control, such as:
- How do we identify the patients who would benefit most from GLP-1 therapy, even if they don’t yet have diabetes?
- How can we address the access gap created by high costs and complex prior authorization requirements?
- What support systems are needed to help patients sustain weight loss or lifestyle changes once therapy begins?
This is an opportunity for providers to collaborate across specialties, adopt holistic approaches to care, and better understand the diverse social, behavioral, and biological factors influencing health outcomes.
Other implications for clinicians include:
Enhanced treatment options for diabetes and obesity
Semaglutides give physicians powerful new tools to help patients manage type 2 diabetes and obesity. Their ability to improve glycemic control and promote weight loss may lead to better long-term outcomes—especially for patients facing multiple metabolic conditions.
Patient education and counseling
With growing media coverage and the perception of GLP-1s as weight loss “miracle drugs,” patient expectations may not always align with clinical reality. Physicians may need to dedicate more time to discussing how semaglutides work, their side effects, and the importance of combining them with lifestyle changes like diet and exercise. Clinicians can set up GLP-1 workflows in their EHR, complete with care plans and resources automatically sent through the patient portal after a prescription is sent.
Patient monitoring and follow-up
As GLP-1 use increases, so too does the need for regular monitoring. You may find that patients on these medications require more frequent check-ins to track response, assess tolerability, and fine-tune dosages. This could lead to more structured follow-up schedules and proactive outreach.
Clinician collaboration for coordinated care
Effective management of obesity and diabetes often calls for a team-based approach. Clinicians may increasingly coordinate with dietitians, endocrinologists, behavioral health professionals, and care managers to deliver holistic care and support patient success.
Shifting treatment paradigms and health outcomes
The demonstrated efficacy of semaglutides in promoting weight loss —particularly Wegovy®, which received FDA approval for weight management in 2021 — may lead to earlier intervention for patients with obesity.2 This shift toward proactive chronic disease management has the potential to reduce downstream complications, improve patient health outcomes and quality of life, and reduce healthcare spending.
Supporting chronic care, addressing disparities
At athenahealth, we recognize that the true impact of trends like GLP-1 growth extends beyond prescriptions. These prescriptions intersect with critical issues in healthcare today: the management of chronic conditions, disparities in access to treatment, and systemic factors like income, geography, and health literacy that shape patient outcomes.
For rural health systems and providers serving underserved populations, GLP-1 prescribing may be influenced as much by local availability and payer policies as by clinical appropriateness. These trends reinforce the importance of addressing social drivers of health (SDOH) as part of an integrated care strategy.
Through the power of the athenaOne network, we’re committed to equipping physicians with real-world insights, not just to understand what’s happening across the country—but to empower better decisions for the communities they serve.
If you're interested in learning more about how athenaOne can help you manage patients with chronic conditions, navigate prescribing trends, or close care gaps, we're here to help.
More athenaInstitute resources
Continue exploring
1. Based on athenahealth data as of Dec. 2024
2. National Library of Medicine, Sept. 2022, Weight Loss Outcomes Associated With Semaglutide Treatment for Patients With Overweight or Obesity; https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9486455/
About the data:
This analysis is based on deidentified patient data from 8,555 athenaOne clients active between 2022–2024, including 55.9 million unique patients who received at least one documented prescription. GLP-1 medications were identified through clinical chart entries using fuzzy text search, and diagnoses were linked via same-year claims for the same patient from the prescribing provider. State-level analysis is based on the primary address of participating athenaOne clients, not individual patients.










